# Connecting with PHP
This guide explains how to establish a connection between a **PHP** application and a **PostgreSQL** database using the built-in `PDO` extension. It walks through the necessary setup, configuration, and execution of a simple SQL query.
### **Variables**
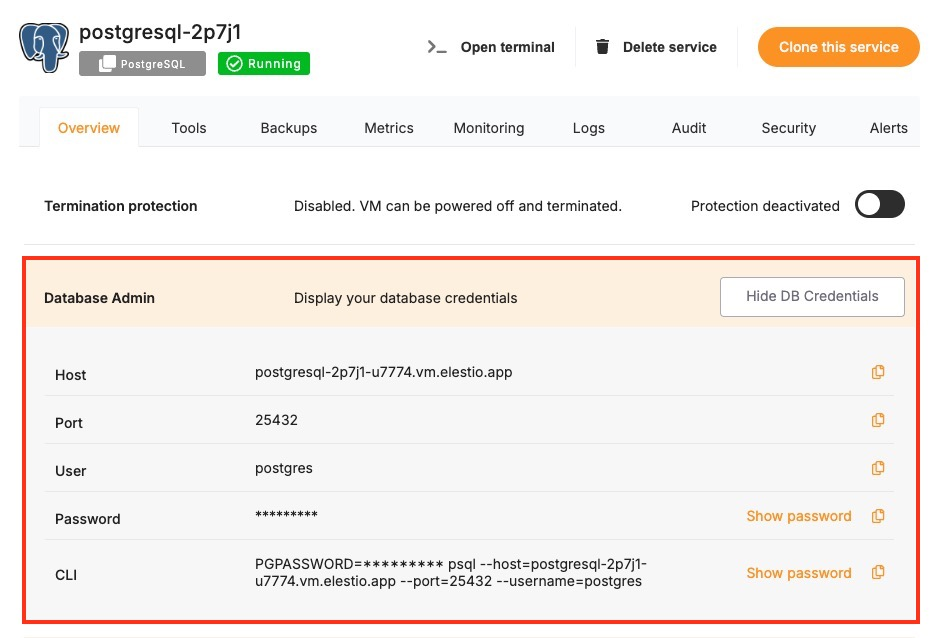
To connect to a PostgreSQL database, you only need one environment variable — the **connection URI**. This URI contains all the necessary information like username, password, host, port, and database name.
Variable
Description
Purpose
**POSTGRESQL\_URI**
Full PostgreSQL connection string (from the Elestio service overview page)
Provides all necessary credentials and endpoint details in a single URI format.
The URI will look like this:
```bash
postgresql://:@:/
```
You can find the details needed in the URI from the **Elestio service overview** details. Copy and replace the variables carefully in the URI example provided above.
### **Prerequisites**
##### **Install PHP**
Check if PHP is installed by running:
```bash
php -v
```
If not installed, download and install it from [https://www.php.net/downloads.php](https://www.php.net/downloads.php).
### **Code**
Once all prerequisites are set up, create a new file named `pg.php` and add the following code and replace the `POSTGRESQL_URI` with actual link or in environment setup as you wish:
```php
query("SELECT VERSION()")->fetchColumn();
echo $version;
```
To execute the script, open the terminal or command prompt and navigate to the directory where `pg.php`. Once in the correct directory, run the script with the command
```kotlin
php pg.php
```
If the connection is successful, the terminal will display output similar to:
```bash
PostgreSQL 16.8 (Debian 16.8-1.pgdg120+1) on x86_64-pc-linux-gnu, compiled by gcc (Debian 12.2.0-14) 12.2.0, 64-bit
```