How to use and deploy Elestio CI/CD Clone template Apps
SoThis tutorial will show you madehow to use our clone template feature in CI/CD. We're going to use a ReactSimple Javascript web applicationapplication, but you can use any template and wantdeploy it in the same way. 🚀
The clone template feature was similar to forking our examples from GIthub and deploying it using an import git repository tab in Ci/CD, but using the clone template was easier because you didn't have to manually fork our template example and then deploy it using our import git repository tab. If you choose a template from the CI/CD clone template feature, Elestio will automatically create an example template repository in your git account and deploy it to the cloudcloud. 🚀In this case, all you need to do is choose the template.
You probably heard about Kubernetes (and all its complexity) or various options to deploy your apps like Heroku, Render Fly, or Railways. They all have something in common, those products are building your own source code on every commit from your GIT repository.
Elestio is doing the same ... but different! Instead of deploying your app to a shared cluster, we deploy to dedicated VMs.
In this tutorial, we will deploy a simple ReactJS app that was created using the create-react-app command. You can use any existing application, create a new one with create-react-app, or simply fork and use our example by following the link.
To learn more about the elestio CI-CD, go here.
If you're new, sign up for Elestio, otherwise, login to your existing account.
Deploy aElestio ReactJs web app with CI/CDapps to the cloud using the CI/CD Clone template feature.
Step 1:
Go to CI/CD from the left sidebar.
Step 2:
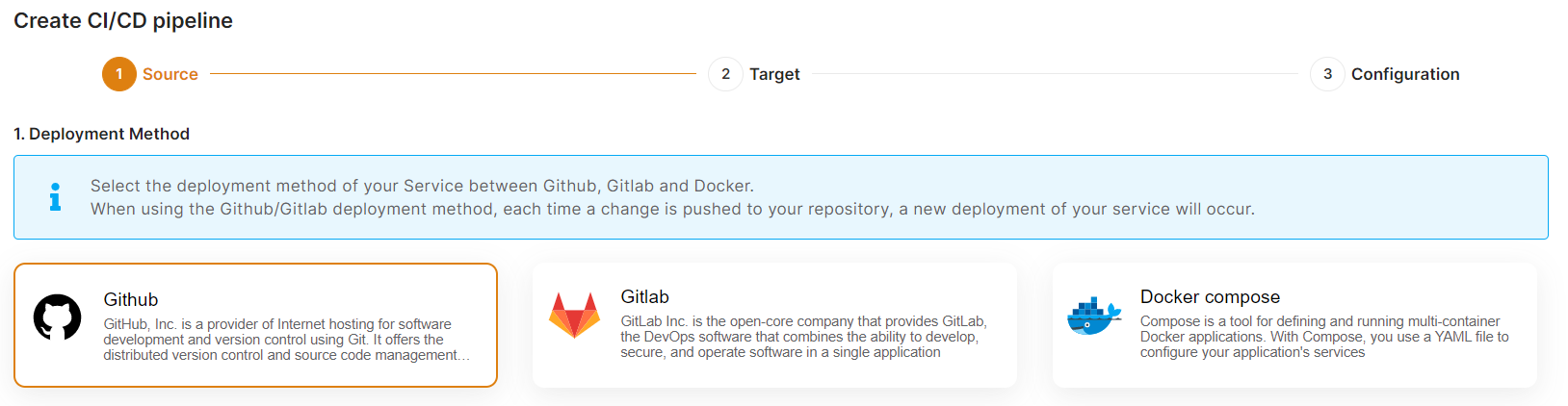
Now, select the deployment source.
In this tutorial, I'm deploying using GITHUB, but you can also use GITLAB if you have a project there.
Step 3:
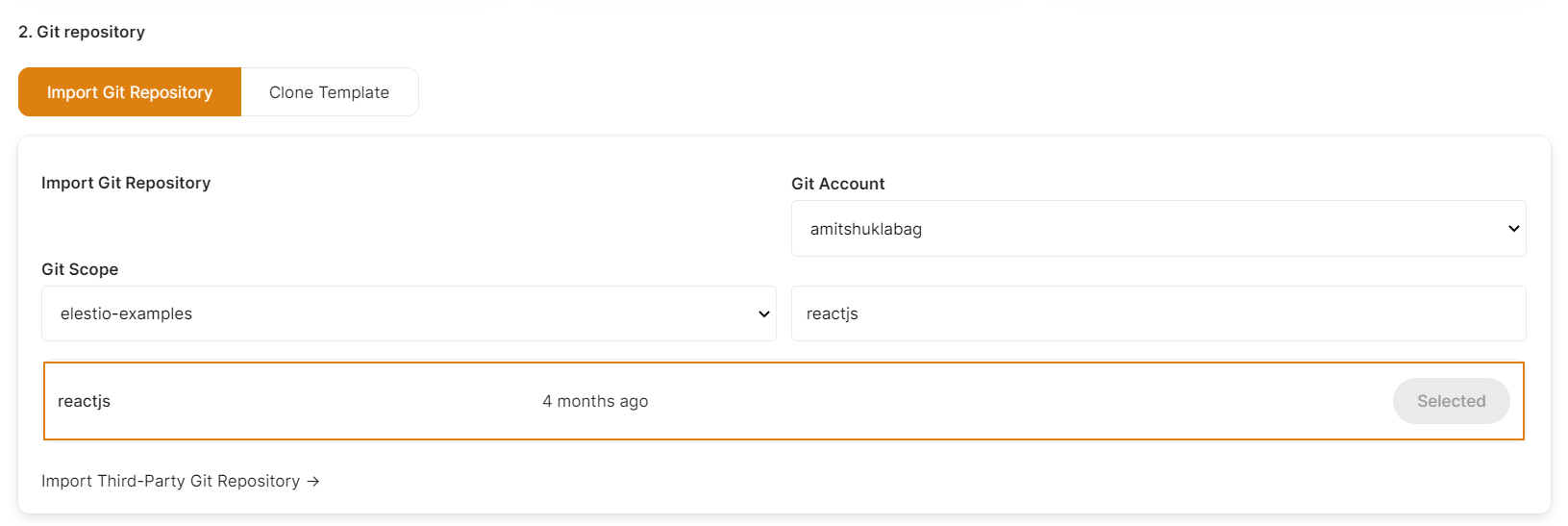
Select the repository.Clone Template Tab.
Here you can see the most interesting and well-liked tech stacks' elestio templates.
As I'm deploying a Static Java Script Web Application, I've chosen these, but you can adopt whatever you want.
If you have already authenticated your GITHUB or GITLAB account in ci-cd for repository access, you can choose the desired repository to deploy directly. Otherwise, you must first authenticate your GIT account with elestio ci-cd for repository access.
Step 4:
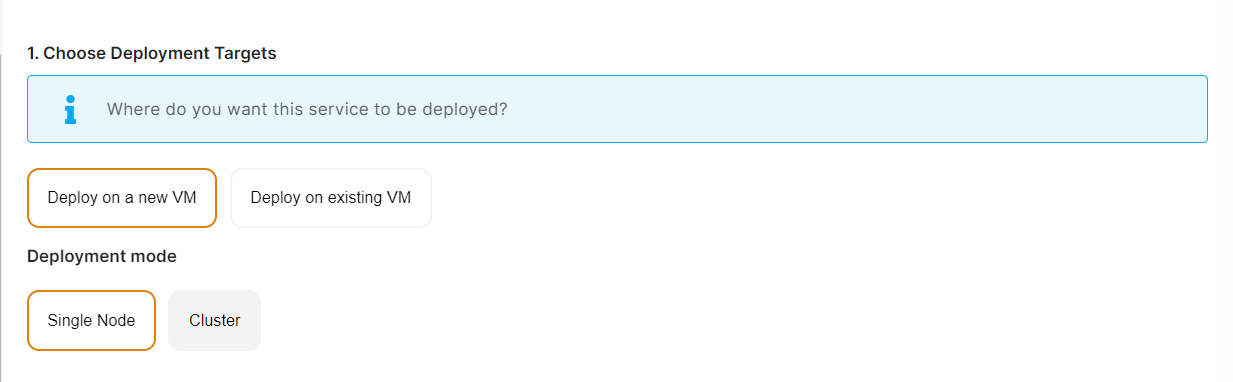
Choose Deployment Targets
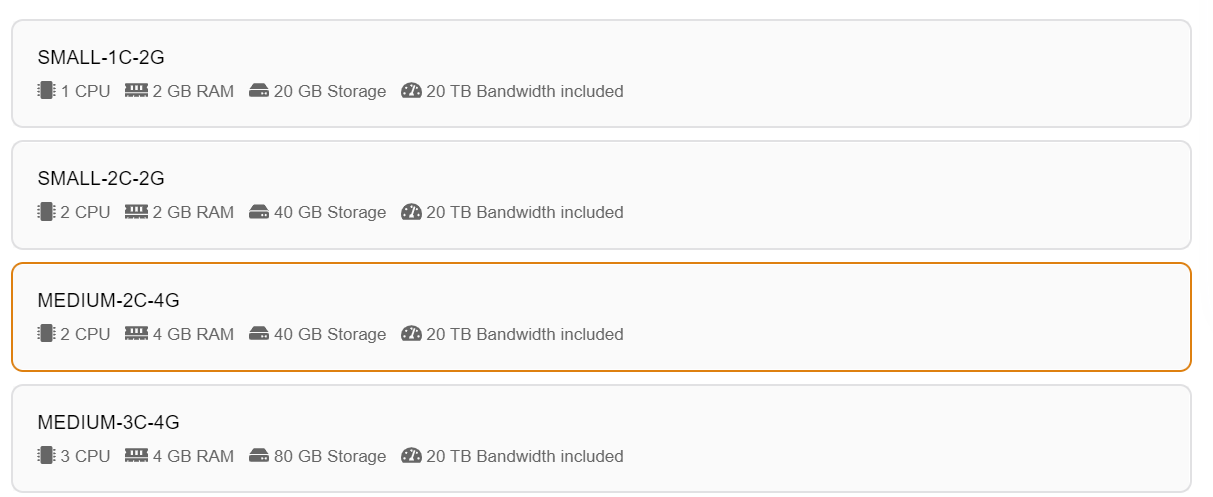
Elestio offers two types of deployment targets "Deploy on a new VM" and "Deploy on an existing VM".
You are allowed to set up n pipelines on each elestio Ci-CD target/VM. According to the project configuration you select and the project you're deploying, the number of pipelines varies.
If you want to deploy these projects as a pipeline on a new Target/VM or don't have any installed targets, choose "Deploy on a new VM." If you already have any installed or previously configured ci-cd targets/VMs, choose "Deploy on an existing VM," and then choose the existing target from the targets dropdown.
Follow the steps below only if you select "Deploy on a new VM," otherwise click the next button to proceed.
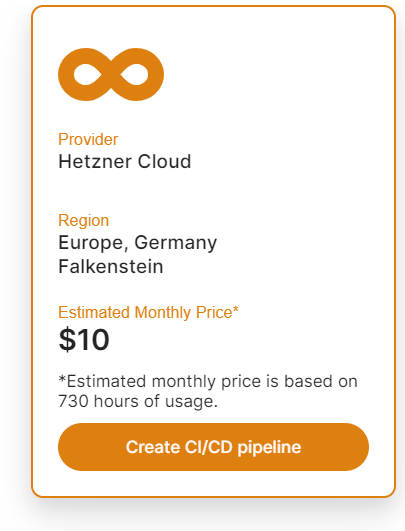
CI/CD Pipelines by Elestio are available with our 5 cloud partners (AWS Lightsail, Digital Ocean, Vultr, Linode & Hetzner) in 85 locations over 27 countries but also on any cloud (AWS, Azure, Google, Oracle, ...) and on-premise with BYOVM.
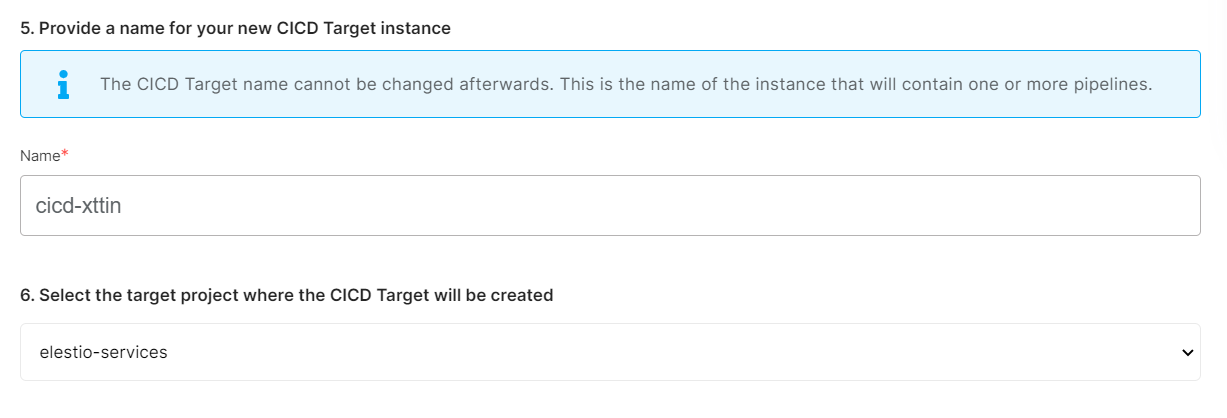
If you want to deploy it with a different name and a different project, you can customize it. By default, we configure it with a dynamic target name and the current project.
Step 5:
Configure your Project
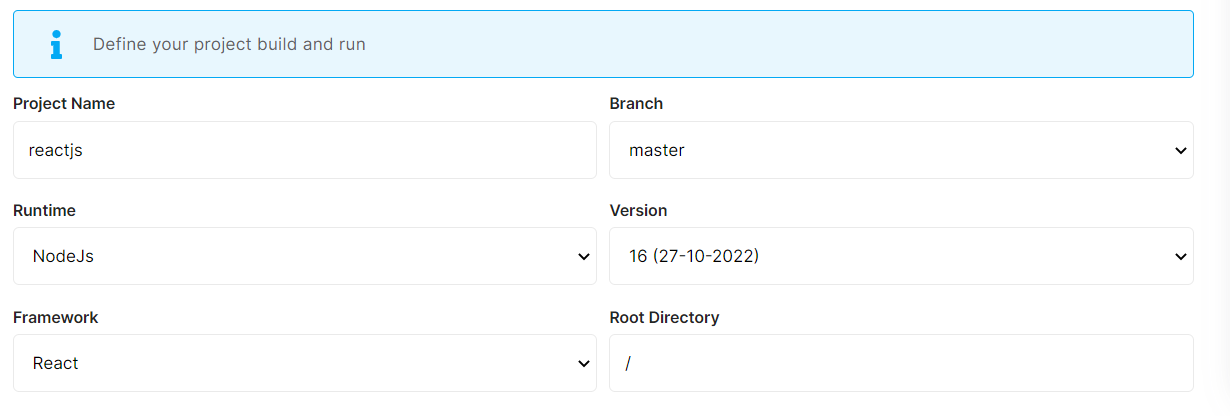
Here you can configure the project details by filling up the project name, branch, run time, version, framework, and root directory.
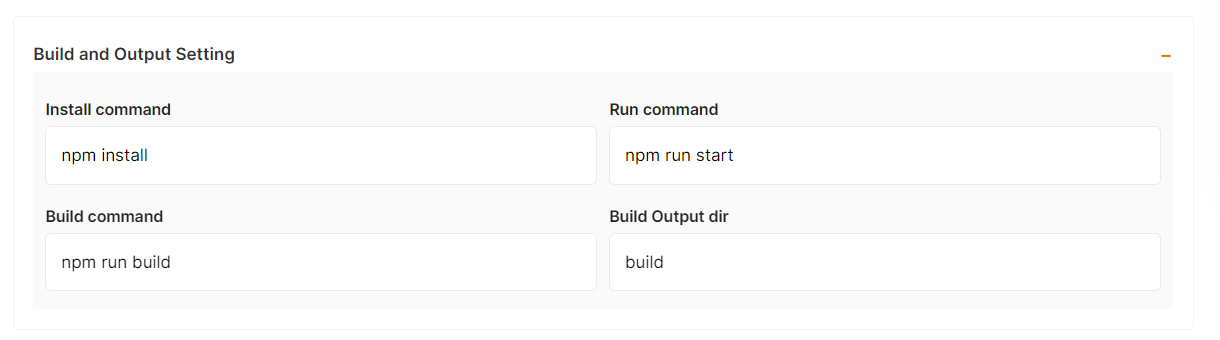
In the Build and output setting, you can configure your project install, run and build command.
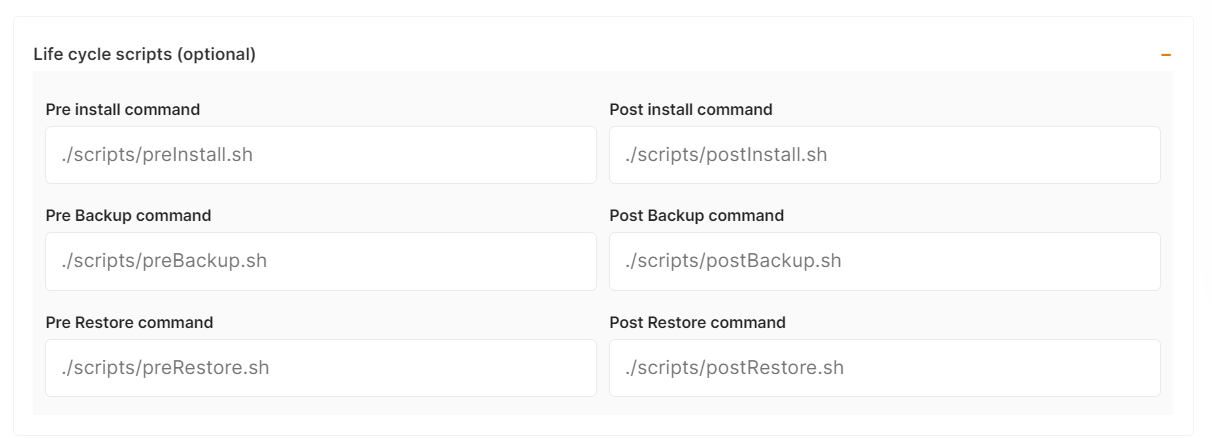
The configuration of life cycle scripts is always optional; they should only be used if you want to execute a specific command before and after building your project. Otherwise, leave them empty.
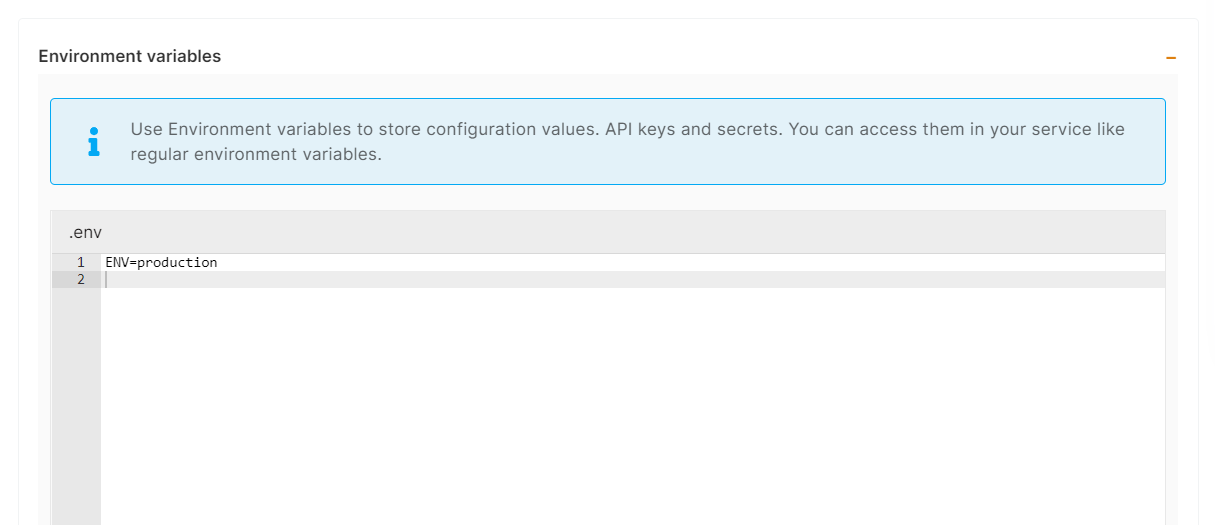
You can list all of your project's API keys and secrets here if they were saved in ENV
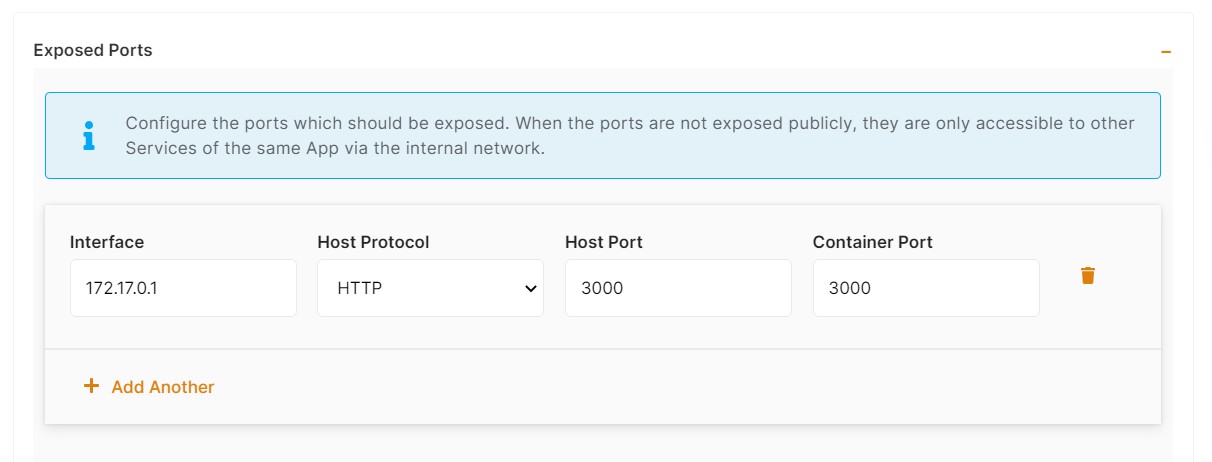
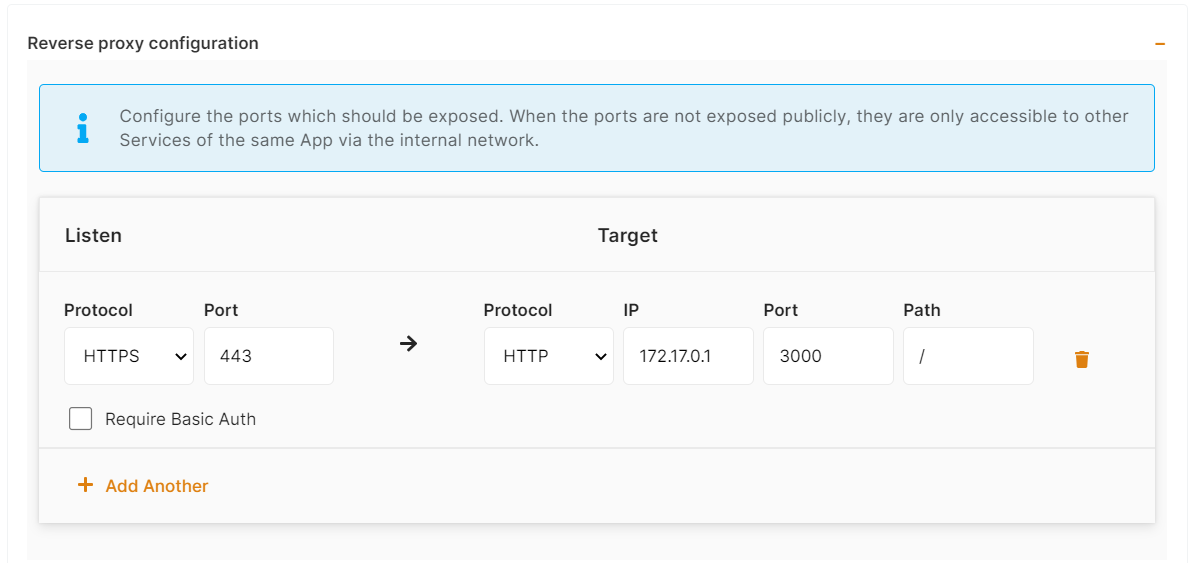
The final step is to configure the exposed port and reverse proxy settings. You can specify the port on which your project will run here.
If your project includes elestio.yml, Elestio will auto-fill all of these fields. As in this tutorial, we're using our ReactJs elestio example, so you can see in the above images that all of our fields are auto-filled.
Refer to these links to learn how to create our own elestio.yml for the project.
A sample elestio.yml for ReactJs is shown below. check it out on github
config:
runTime: 'NodeJs'
version: '16'
framework: 'React'
buildCommand: 'npm run build'
buildDir: 'build'
runCommand: 'npm run start'
installCommand: "npm install"
icon: "src/logo.svg"
screenshot: "src/screenshot.png"
ports:
- protocol: "HTTPS"
targetProtocol: "HTTP"
listeningPort: "443"
targetPort: "3000"
targetIP: "172.17.0.1"
public: true
path: "/"
isAuth: false
login: ""
password: ""
environments:
- key: 'ENV'
value: 'production'
webUI:
- url: "https://[CI_CD_DOMAIN]"
label: "Website" Step 6:
Click the Create CI/CD pipeline button to deploy your pipeline.
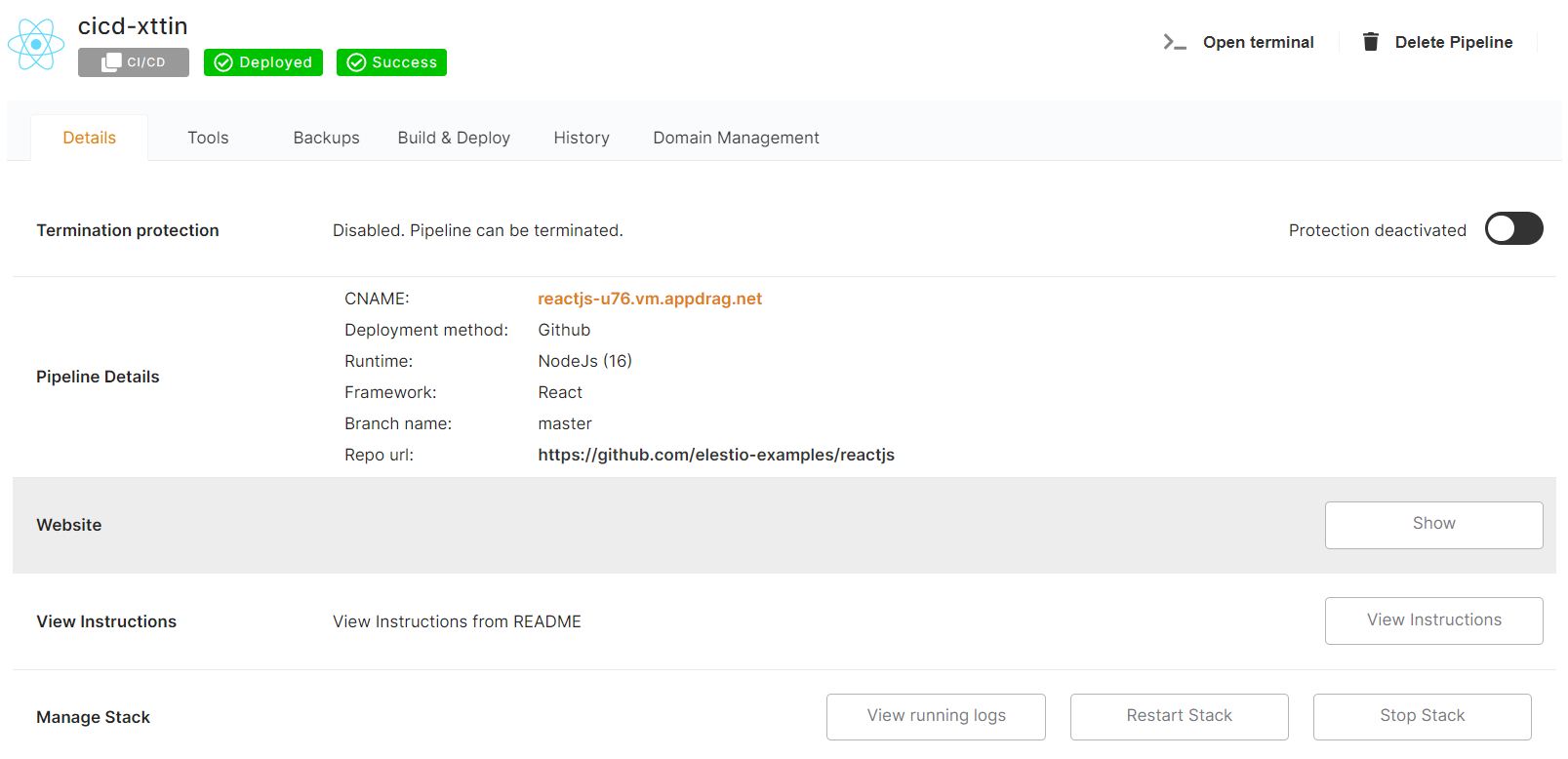
In a couple of moments, your application was successfully deployed on elestio 🚀.
You can now view your deployed URL and access your application by going to desired application pipeline details.
Please let us know by contacting our support email or ticketing system if you give it a shot and encounter any problems or if anything goes wrong.
Join us on discord to know more.