Connecting with Java
This guide explains how to establish a connection between a Java application and a KeyDB database using the Jedis library. It walks through the necessary setup, configuration, and execution of a simple KeyDB command.
Variables
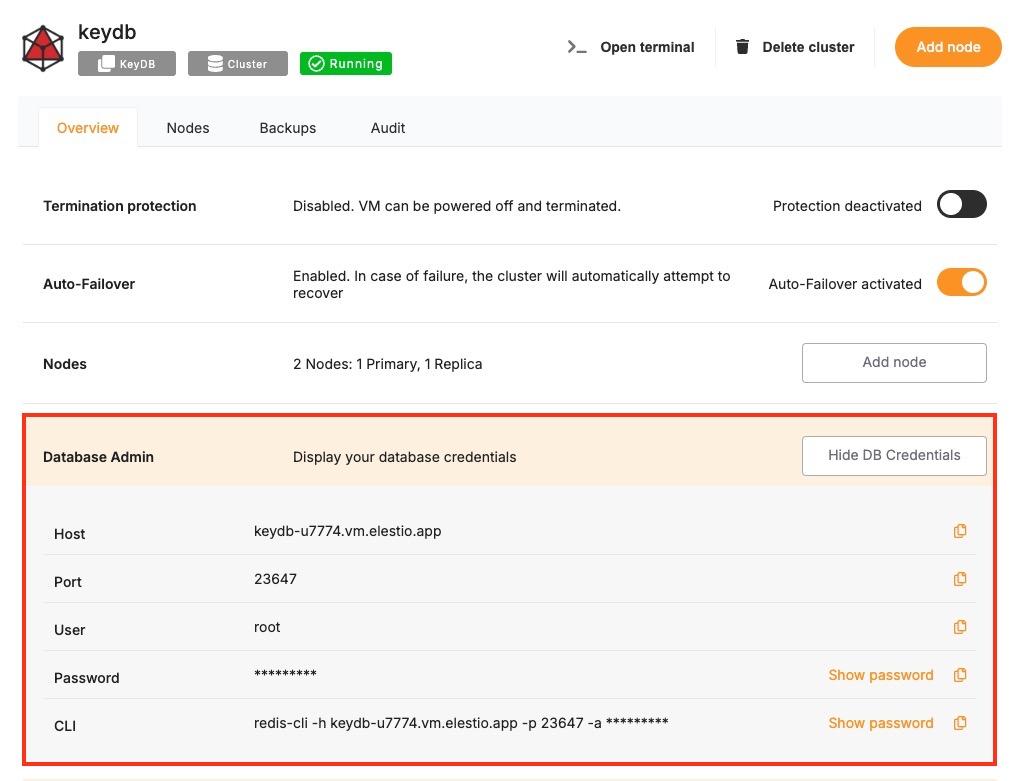
Certain parameters must be provided to establish a successful connection to a KeyDB database. Below is a breakdown of each required variable, its purpose, and where to find it. Here’s what each variable represents:
|
Variable |
Description |
Purpose |
|---|---|---|
|
|
KeyDB hostname, from the Elestio service overview page |
The address of the server hosting your KeyDB instance. |
|
|
Port for KeyDB connection, from the Elestio service overview page |
The network port used to connect to KeyDB. The default port is 6379. |
|
|
KeyDB password, from the Elestio service overview page |
The authentication key required to connect securely to KeyDB. |
These values can usually be found in the Elestio service overview details as shown in the image below, make sure to take a copy of these details and add it to the code moving ahead.
Prerequisites
Install Java
Check if Java is installed by running:
java -versionIf not installed, download it from oracle.com and install.
Download Jedis and Dependencies
The Jedis library enables Java applications to interact with KeyDB. You need to download two JAR files manually:
-
Jedis JAR (Jedis 5.1.0):
https://repo1.maven.org/maven2/redis/clients/jedis/5.1.0/jedis-5.1.0.jar
-
Apache Commons Pool2 JAR (Required by Jedis):
https://repo1.maven.org/maven2/org/apache/commons/commons-pool2/2.11.1/commons-pool2-2.11.1.jar
Place both JAR files in the same directory as your Java file.
Code
Once all prerequisites are set up, create a new file named KeyDBTest.java and add the following code:
import redis.clients.jedis.JedisPooled;
public class KeyDBTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String host = "HOST";
int port = PORT; // e.g., 6379
String password = "PASSWORD";
JedisPooled jedis = new JedisPooled(host, port, password);
try {
jedis.set("testKey", "Hello KeyDB");
String value = jedis.get("testKey");
System.out.println("Connected to KeyDB");
System.out.println("Retrieved value: " + value);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("KeyDB connection or operation failed: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
}To execute the script, open the terminal or command prompt and navigate to the directory where KeyDBTest.java is located. Once in the correct directory, run the following commands:
On Linux/macOS :
javac -cp "jedis-5.1.0.jar:commons-pool2-2.11.1.jar" KeyDBTest.java
java -cp ".:jedis-5.1.0.jar:commons-pool2-2.11.1.jar" KeyDBTestOn Windows :
javac -cp "jedis-5.1.0.jar;commons-pool2-2.11.1.jar" KeyDBTest.java
java -cp ".;jedis-5.1.0.jar;commons-pool2-2.11.1.jar" KeyDBTestIf the connection is successful, the terminal will display output similar to:
Connected to KeyDB
Retrieved value: Hello KeyDB